To get seedlings of early vegetable varieties or grow heat-loving crops in a cool climate, you can’t do without a greenhouse. Of the many different greenhouse constructions, you can choose the most suitable model for your site. This article will introduce you to a single-pitch greenhouse and tell you how to build it yourself.
Design features of a single-pitch greenhouse
As in other similar structures, racks for flower pots can be installed in a single-slope greenhouse, or land beds for vegetable crops can be poured. It differs in its design: it has only one slope, due to which the walls turn out at different heights. Such a structure is usually located with one wall to a hill or attached to the wall of a house or fence.
Advantages
The pitched greenhouse has a number of significant advantages.
- These include:
- compact design, especially wall-mounted, which allows rational use of space on a small land plot;
- frugality, because for building at the main wall of the house less building materials are needed;
- it is easier to conduct communications from home (electricity, water);
- a pitched roof does not delay precipitation (rain, snow);
- easy to heat due to the proximity to the heated house and small space;
- reliability thanks to fastening to a capital wall;
- protection by the wall of the house from strong winds and frosts;
- time saving, i.e. a single-pitched construction is faster to assemble than a gable.
Disadvantages
- It is worth mentioning the disadvantages of such a structure:
- lack of usable area for tall cucumber and tomato bushes, more suitable for growing seedlings with subsequent transplantation to a permanent place;
- the wall of the house closes on one side of the sunlight;
- construction near a residential building must be carried out carefully so as not to damage communications.
Did you know? Residents of many northern countries attach greenhouses to their homes. It is not only economical and practical, but also beautiful, because you can go out into the greenhouse at any time and relax there, surrounded by plants and flowers.
Choosing the optimal size of the greenhouse and the right materials
The dimensions of the future greenhouse largely depend on the material capabilities of the owner. To choose the optimal size of a building, it is necessary to determine its 4 dimensions: the length, width, height of the rear and front walls. Width and length are calculated depending on the number of planned landings. The room should also have enough space to freely pass between plants or beds, easily care for them and harvest. The width usually varies from 2 to 4 m, and the length should not be more than the wall of the adjacent house.
When calculating the height, you also need to consider several factors. The back wall should not be higher than the wall of the house. And the maximum height of the planned plants, their temperature and the growth of the host, so that he is comfortable to work, affects the height of the outer wall. The usual average sizes are 210–250 cm and 160–180 cm.
The choice of materials also depends on the budget and type of construction (temporary collapsible and light, or winter, reliable and strong). For the frame of the greenhouse, they most often use:
- wooden bars, easy to use, strong and beautiful, but they need protection from moisture, insects and rot;
- profiled metal pipesreliable and durable, which are suitable for stationary buildings;
- plastic profiles, light and cheap, easy to use, but less reliable than metal and wood, are more suitable for summer buildings.

How to build a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands
When all the calculations are completed, a drawing is made and the necessary building materials are purchased, you can begin construction. The southern wall of the house, garage or barn will be the best place for wall construction. Before you get down to business, the selected area should be cleaned of debris and weed grass and smoothed as much as possible with a shovel.
Foundation selection
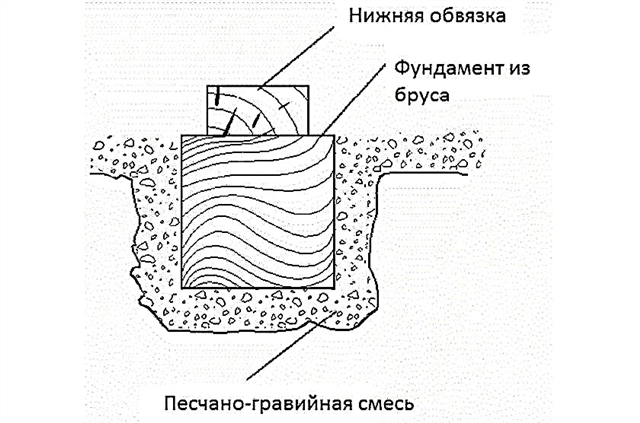
From the purpose of the greenhouse and its design depends on what material it is better to build a foundation:
- concrete base - a strong and reliable foundation, will keep a winter greenhouse for many years, but an expensive option;
- a box of wooden bars - more affordable and simple design, designed for seasonal greenhouses made of lightweight materials;
- column foundation or base without foundation - buried in the ground and fixed piles (wooden bars or iron pipes), to which the light frame of a summer greenhouse or greenhouse is attached.
 A greenhouse with a shed roof does not need to be located only at the house or fence - there are buildings that stand separately
A greenhouse with a shed roof does not need to be located only at the house or fence - there are buildings that stand separately
Step-by-step instructions for building a wooden foundation:
- Mark the borders of a rectangular foundation.
- Along the perimeter, dig a trench with even walls and a bottom, the depth and width of which corresponds to the size of the bars.
 If possible, you can use special equipment
If possible, you can use special equipment - Fill a trench with sand and gravel by a third.
- Cut the bars with a section of 100 × 100 mm or 150 × 150 mm of the desired length and treat them with an antiseptic.
- Connect the bars in one box, fastening them with corners and screws, you can apply the connection "in the paw" or "in the floor of the tree."
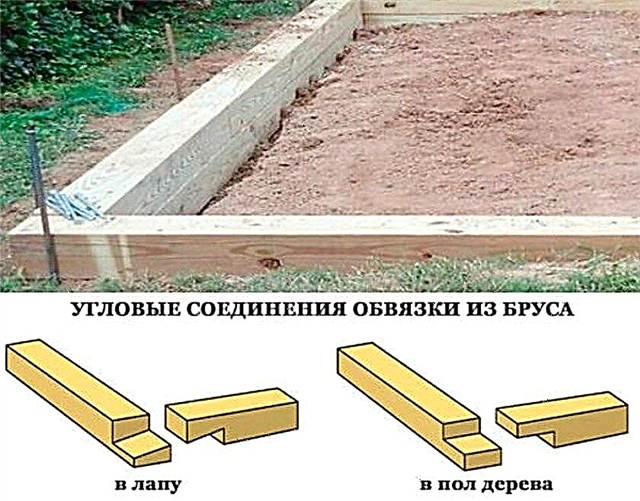
- Lay the box in the trench, aligning it horizontally.
- Fix this structure with iron pins 50–70 cm long, driving them into the ground at the corners from the inside.
Important! For the foundation, it is advised to take timber from larch. They are more durable and less deteriorate from moisture.
End assembly
All parts of the frame can be assembled separately, and then connect them by attaching to the foundation. For a wall greenhouse, in which the height of the back wall is 252 cm, the front - 152 cm and the width of the end - 173 cm (dimensions can be different), To collect the side walls you will need:
- timber with a slice of 50 × 100 mm and a length of 236 cm - 2 pcs.;
- the same bar 196 cm long - 2 pcs.;
- timber 69 cm long - 2 pcs.;
- jib 163 cm long - 2 pcs.;
- crosspiece 61 cm long - 3 pcs.;
- crosspiece 26 cm long - 4 pcs.
For fasteners use corners and screws. All bars and cross-members of the end walls must be assembled according to the drawing:
In one of the side walls you need to make the doors of the beams 50 × 100 mm. Required Items:
- vertical bars of 187 cm - 2 pcs.;
- crossbars of 42 cm - 3 pcs.;
- door hinges - 2 pcs.
 Doors need to be assembled, and after collecting the entire greenhouse - hang on hinges
Doors need to be assembled, and after collecting the entire greenhouse - hang on hinges
Frame assembly
The outer and rear walls are assembled from beams with a section of 50 × 100 mm. Of them you need to cut parts of different lengths:
- loungers, upper and lower, 508 cm long (greenhouse length) - 4 pcs.;
- vertical cross-pieces for an external wall 152.4 cm high - 12 pcs .;
- vertical crossbars for the rear wall 252 cm high - 12 pcs .;
- horizontal crossbars for fastening vertical bars 42 cm long - 22 pcs.
 The vertical crossbars of the rear part must be cut off from the upper edge by 30 ° for the roof slope
The vertical crossbars of the rear part must be cut off from the upper edge by 30 ° for the roof slope
Wall Assembly:
- Between the rods, the upper and lower, at a distance of 42 cm, vertical crossbars must be placed (short for the front part, long - for the wall part). Make sure that the ends of the long crossbars cut off by an angle are attached to the upper back wall.
- Fasten them with corners and screws.
- Secure each wall with horizontal cross members.

Finished walls must be installed on a wooden base, fastening to it with screws at a right angle. The back wall should stand close to the house, attached to it by boards. All slots must be filled with mounting foam.
Important! Before assembling the frame, all wooden blocks must be covered with special means that repel insects and protect against mold and rot: resin, dyeing impregnation or other bioprotective agents.
The roof is also assembled from beams of 50 × 100 mm. Of them you need to do:
- rafters 187 cm long - 12 pcs.;
- crossbars 42 cm long - 22 pcs. (11 for the central bond and 11 for the ridge).

Rafters are connected to the crossbars by corners and self-tapping screws. The ends of the rafters must be cut at an angle for a tight connection with the upper walls of the walls: adjacent to the wall of the house - 30 °, to the front wall - 60 °. Now the roof is laid on the upper beds and attached with screws. Then the side walls are installed.
We must not forget to make 2-3 ventilation windows in the roof. They are made of thin beams with a cross section of 50 × 50 mm, located between the rafters and fixed on loops.
Frame cladding
The best greenhouse designs are made from polycarbonate.
- It has several advantages that film and glass do not have:
- transmits sunlight well and distributes it throughout the interior;
- protects from ultraviolet rays;
- easily withstands high and low temperatures;
- holds heat well;
- Lightweight and easy to use material.
Did you know? Polycarbonate was accidentally invented by German chemists in the early 1950s. and due to its lightness and strength, it was used in the manufacture of parts for aircraft, spaceships and military equipment. And the first greenhouses made of cellular polycarbonate appeared in the 1970s. in Israel.
What to do:
- Carefully cut the polycarbonate sheets with a construction knife into pieces of the desired size.
- Seal the ends of the sheets with special adhesive tapes: the top edge is a sealing tape, and the bottom edge is a perforated tape. Due to this, condensate will not accumulate inside.
- Drill holes for thermowells with a margin of 2 mm at a distance of 4–5 cm from the edge.
- To the frame attach a sheet of polycarbonate so that the protective layer is outside and the honeycombs are located vertically.
- Insert the thermal washers into the holes and tighten the screws, but without pulling so that the sheet does not bend or burst.
- The sections of the two sheets to connect the docking profiles.
- Attach all sheets in the same way.
- Fill the gaps with foam.
- Carry out communications. The greenhouse is ready.

Greenhouse Care and Maintenance Tips
Polycarbonate is a fragile material, it needs delicate care to remain intact. In order for the greenhouse to function smoothly for many years, you need to take care of it according to the season:
- in spring - a general cleaning is carried out before a new sowing, which includes washing the polycarbonate inside and out with water, a rag and a soap solution (coarse brushes and cleaning agents must not be used so as not to damage the surface);
- in summer - if it is very hot, you can make shading with a covering material or spray the walls and roof of the greenhouse with a chalk solution that is easily washed off with water from a hose;
- in the fall - remove the remains of all plants, disinfect the soil with special means and make fertilizers;
- in winter - you need to make sure that the snow does not linger on the roof and that snowdrifts do not accumulate against the walls, you need to sweep it off with a soft broom to avoid scratches on the surface, you can cover the beds inside with a layer of snow to moisten it.
From all of the above it follows that it is not difficult to build a polycarbonate greenhouse with a shed roof. And following the tips and instructions given above, even a beginner will cope with this.

 If possible, you can use special equipment
If possible, you can use special equipment