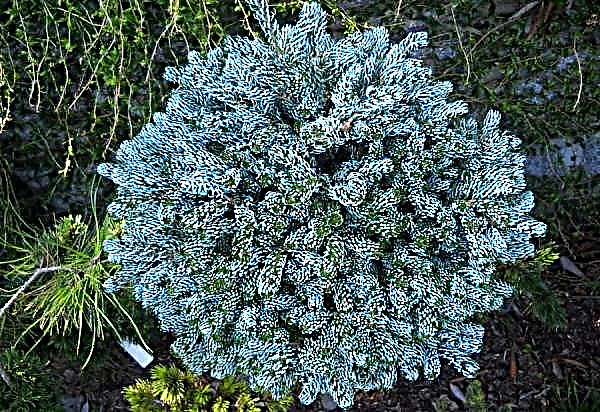
Those wishing to decorate their garden with an evergreen should pay attention to thuja. This culture has many advantages, including winter hardiness, resistance to polluted air, longevity, as well as bright colors even in winter.
Conditions for the growth of thuja
In order for the plant to have an attractive and decorative look, it is necessary to create the necessary conditions for it:
- Good lighting and protection from the scorching midday sun. In open areas under sunlight, the culture loses moisture and becomes vulnerable in the winter. In the shade, the color of the needles becomes faded.
- Protection against wind and draft.
- No stagnation of water.
- The most suitable soil composition is a mixture of turf, sand and peat. The soil should also be neutral or slightly acidic, breathable and moderately moist.
- The landing pit should be 30–40 cm wider and 20 cm deeper than an earthen lump with roots.
- The root neck should be at or slightly above ground level. If it is too deep, the tree will hurt and may die. Too high a location of the root neck will provoke drying out.
- The distance between neighboring specimens for tall varieties is 4–5 m, for undersized ones - from 1 to 2 m, and in hedges - 1 m regardless of variety.
- It is useful to sprinkle the trunk circle with a mulching layer, which will protect the earth from drying out and relieve weeds.

Incorrect landing and care and correction
Yellowing of needles in thuja can cause natural, agricultural or biological factors. The cause of natural yellowing may be any weather changes or season changes. The source of agrotechnical violations is improper planting or caring for the plant. And biological factors are manifested in the impact on the culture of various insects, microorganisms or animals.
Important! Final feeding is carried out in August. Later application of fertilizers can stimulate active growth, and unripe shoots will not tolerate winter frosts.
Yellowing and drying of thuja branches can cause the following reasons:
- Too deep or shallow fitin which the root collar is either heavily sprinkled with soil, or is located high above its surface. In this case, yellowing of the crown will appear on the 2nd – 3rd year after planting. According to the rules, the root collar should be placed at the level of the upper layer of the earth. You can try to fix this problem as follows: to dig out part of the soil from the trunk with strong deepening or, conversely, sprinkle soil with a high landing.
- A thickened planting that causes permanent shading by trees of each other. After 4–5 years, sprouted roots begin to compete with each other in the extraction of nutrients, which can also trigger yellowing and drying processes. It is unlikely that it will be possible to correct this situation, as adult specimens do not respond well to transplantation, and this work is too time-consuming. You can try to regularly make a sufficient amount of top dressing and periodically remove dried shoots.

- Change of place of growth, for example, a transplant from shaded to a sunny area. Conifers respond to such changes with the appearance of yellow. But after a while, the thuja can restore its normal color, although it is better to avoid such sudden changes.

- Improper care of a young seedling. While the tree does not take root, it must be protected from scorching rays and watered every week for 10 liters for each instance, and in drought - 2 times a week for 15 liters. Spraying the crown, which should be carried out in the evening or morning hours, will help revive the seedling in the heat.

- Excessive or insufficient watering. Lack of moisture, as well as its excess, is harmful to thuja. When the soil dries up, it is required to increase the number of irrigations, and when waterlogging, to reduce. Seedlings should not be planted in lowlands where accumulation of melt or rain water is possible.

- Nutrient deficiency. With a lack of magnesium or potassium, yellowing of the crown tops is observed. Individual branches acquire yellowness (or discoloration) with iron deficiency, so adult specimens need regular top dressing. For fertilizing with minerals, Biode, Kemira-universal, Epina solution and others are used according to the instructions. As organics, an infusion of manure (1: 4), aged for 10–14 days, is used, which is used to pour a near-stem circle at the rate of 3 liters per plant.

Recently, it has become fashionable to grow thuja not only on the street, but also in flowerpots in the room. When growing such decorative varieties, you can also encounter problems when the needles can turn yellow, dry and fall. Some reasons and methods for solving them are similar to those of street copies, but there are also different ones.
In order to avoid unpleasant moments with yellowing and dropping needles, it is necessary to adhere to the basic principles of growing and caring for this coniferous beauty:
- After the thuja adapts a little (10-14 days after acquisition), it needs to be transplanted.
- When transplanting, the new tank should be 2-3 cm larger than the previous one. Thuja has long roots, so the pots are selected high.
- Purchased soil should be for coniferous crops. Do not forget about the drainage layer.
- The location of the tree should be well lit, but protected from midday scorching rays.
- Do not allow drying or strong overmoistening of the soil substrate. Young specimens are moistened after drying of the topsoil, and large specimens are moistened upon drying to a depth of about 5 cm.
- Thuja is a coniferous representative, unpretentious to temperature, therefore in warm time it can be in the temperature range +18 ... + 30 ° С. But in winter, the temperature should not be higher than + 15 ° C. The best place for wintering is a glazed loggia or balcony. The plant reacts poorly to outgoing heat from batteries and other heating appliances.
- In winter, a cool plant is watered 1-2 times a month. At a temperature of about 0 ° C, arborvitae are not watered.
- In winter, thuja do not fertilize, and from spring to the beginning of autumn once a month they make fertilizing for conifers.
 Thuja is easier to tolerate drying of the soil than waterlogging.
Thuja is easier to tolerate drying of the soil than waterlogging.Diseases and their treatment
The appearance of a coniferous plant is often affected by various diseases, among which the most common:
- Phytophthora - affects the root system of the plant. In this case, the thuja wilts, acquires a gray tint, and the bottom of the trunk softens. The reason most often is severe waterlogging. At the same time, helping the thuja is almost impossible. As prevention, fungicides are used according to the instructions.

- Brown shute - a fungal disease that appears on the needles after the snow melts. The dead foliage is covered with a gray cobwebbed coating. At the same time, thin branches die off, and the brown needles can not fall for a long time. Prevention and control measures include spraying in late autumn and after snow melt with Kurzatom (0.7%) or copper chloroxide (0.5%). In spring, with an interval of 10 days, they are treated with Fundazolum (0.2%). Affected fungus branches must be removed and burned.
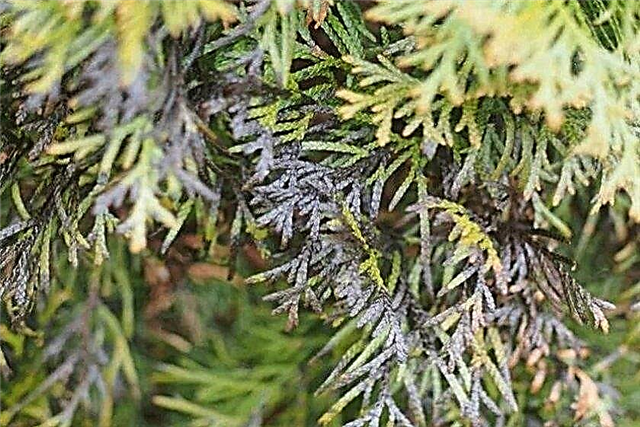

- Pestalocium wilting - Another fungal disease, as a result of which the tips of the shoots with needles become covered with brown spotting and die. Later, black sporangia of mushrooms appear on the needles and they turn gray. For prophylaxis in early spring, treatments are carried out with 0.7% Kurtazom, and for treatment, spraying alternately with Strobi (0.04%), Fundazolum (0.02%) and Bayleton (0.15%). The infected branches are disposed of in the same way as in the previous case.

- Browning shoots - also has a fungal nature and appears in early spring. It appears in the yellowing of the scales, and at the last stage the whole shoot dies. For prevention, a 2% solution of Fundazole is used, which plants are sprayed from July to October with an interval of 2 weeks. To prevent the spread of the disease, it is recommended to immediately remove and burn detected diseased branches.

Pests and the fight against them
Thuja owners often have to take various measures to save their beauties from the invasion of pests.
The most dangerous and common are the following insects:
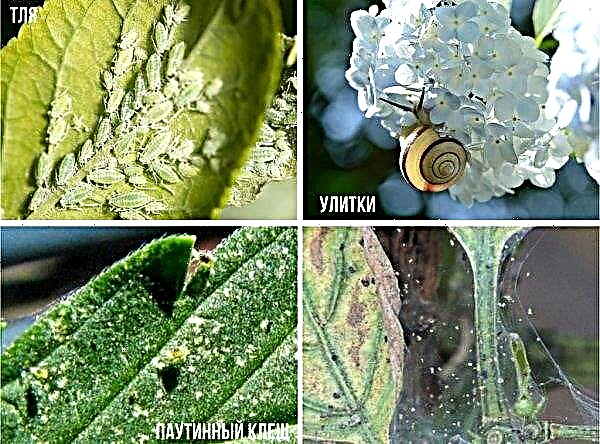
- Aphid - causes damage to the lower part of the branches, manifested in yellowing, and then drying and falling of the needles. This pest is small and gray-brown in color with a whitish-silver coating. The methods for controlling aphids include treatment with insecticides (Aktara, Aktellik, Enzhio or others) according to the instructions.

- Thuja Mining Moth - affects the tops of the shoots, causing their yellowing. This butterfly is about 4–5 mm in size, has brown front wings with silver stripes and dark gray hind wings. The insect begins its flyby in early June, and the larvae gnaw through peculiar passages in the branches and needles, thereby causing great harm to the plant. In order to prevent moth damage, trees need to be sprayed with insecticides, as in the previous case.

- Spider mite - has a round small body yellow, red or orange, covered with sparse bristles. First, it settles on the lower part of the leaves, as indicated by the bright yellow dots on the surface, and then moves to the upper part. The needles turn brown and crumble, and the branches are covered with cobwebs. Vermitek, Fitoverm or Aktofit are effective in controlling this pest. It is necessary to carry out several sprayings with an interval of 14 days.

- Tuevaya hooter - holes in the bark of trees testify to his presence. You can get rid of an insect with the help of insecticides. And the use of Bordeaux fluid will help for preventive purposes.

Other possible causes
In addition to the previously mentioned reasons for yellowing and drying of thuja trees, there are several more:
- Drying and overheating of the near-trunk territory in summer and freezing in winter. To avoid this, it is necessary to mulch the earth around the plants. A layer at least 5 cm thick can be made from sawdust, compost, wood chips or peat.

- Spring damage to the coniferous part by sunlight. After wintering, the plant is weakened, and light streams reflected from the snow (which increases their intensity) can cause burns. For this reason, in February, you need to slightly shade the plants. You can not use spanbond, as it passes the most harmful UV. You should also not use dense fabrics and wrap too much thuja. For protection from the sun, lightweight materials like gauze or mosquito nets are quite suitable. If time was lost and the needles began to turn yellow, then the coniferous plant should be watered with warm water and treated with the Eco-Gel-Antistress biostimulator, and in the beginning of summer, dried branches should be removed.

- Frosts above -30 ° C can also cause yellowing of needles and death of branches. In this case, shelter for the winter is practiced not only in young specimens, but also in older plants.

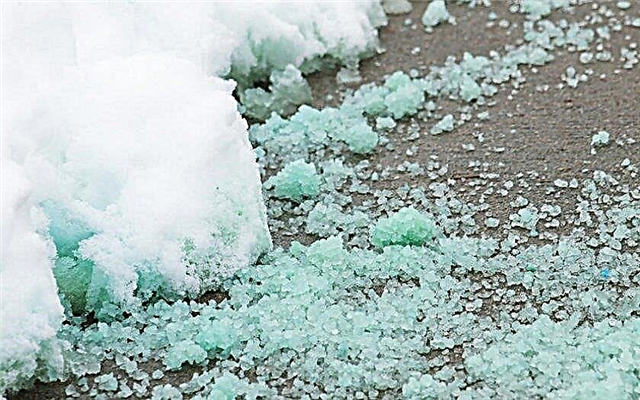
- Various chemicals used against snow and ice are dangerous for conifers. They are capable of causing burns at the ends of branches, which lead to their death, therefore, when processing, care must be taken to prevent such substances from falling onto plants.

- The habit of some animals to “mark” their territory badly affects all plants, including thuja. The urine of cats and dogs can cause yellowing and drying out of branches, especially if these are young seedlings.

Disease and Pest Prevention
Plant diseases, as well as damage by various pests, are easier to prevent than to deal with their treatment later.
Important! In order to retain moisture, the following method is practiced: moss is divided into small pieces and, after mixing with the ground, crumbles around thuja.
To do this, you must follow some rules:
- use only healthy specimens for planting;
- adhere to recommendations for proper watering and timely feeding;
- take measures to protect trees from sunlight and severe frosts;
- regularly prune parts of plants affected by diseases and pests;
- systematically remove weeds and loosen the near-trunk territory;
- carry out preventive treatment with appropriate drugs.

Adhering to the tips and recommendations given in the article, you can grow and have in your house or garden an evergreen beauty thuja that will delight you and your household for many years.































