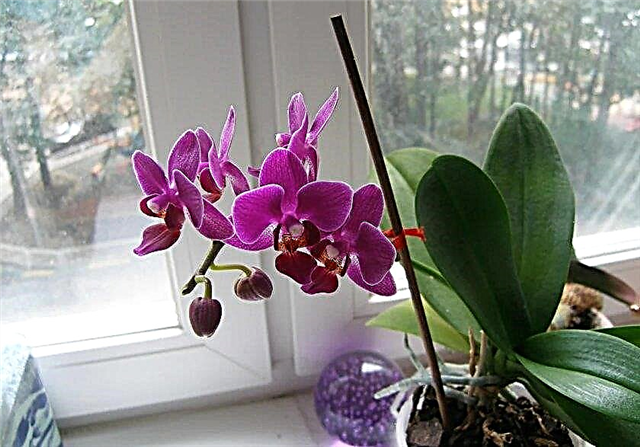
Orchids during flowering are an unusually decorative flower and have many admirers. To receive a blooming orchid as a gift is pleasant for many girls or women; it will adorn almost any celebration. The orchid blooms for a long time, but sooner or later its color will fade, leaving behind an arrow of a peduncle. Consider what to do when the orchid has bloomed, what kind of care should it provide and what are its features.
Dates and features of flowering orchids
Young orchids bloom for 2–4 years of age, if received from children, and for 4–5 years with seed reproduction. First, a young plant pampers its owners with flowering once a year. Flowering itself lasts depending on the type and temperature regime - from 2 weeks to 2 months.
Important! A well-developed plant of some species, with proper care, can please with repeated flowering, but you should not get it from a weak or too young flower, as this can deplete it. Re-blooming orchids should have a well-typed green mass.
Consider the possibility of flowering different types of orchids:
- Phalaenopsis. With proper care, its flowers can be admired year-round. Usually, 2-3 blooms per year are obtained from it, each can take 4-8 months.

- Dendrobium Nobile. It usually blooms 1 time in winter for 3-4 months. Some varieties and hybrids bloom more than once a year, and flowering can be continuous.
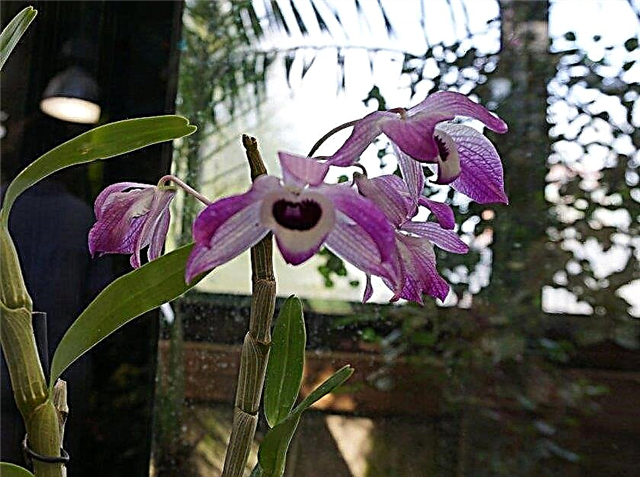

- Cattleya. Blooms once a year for about 3 months. Usually flowering is observed in winter.
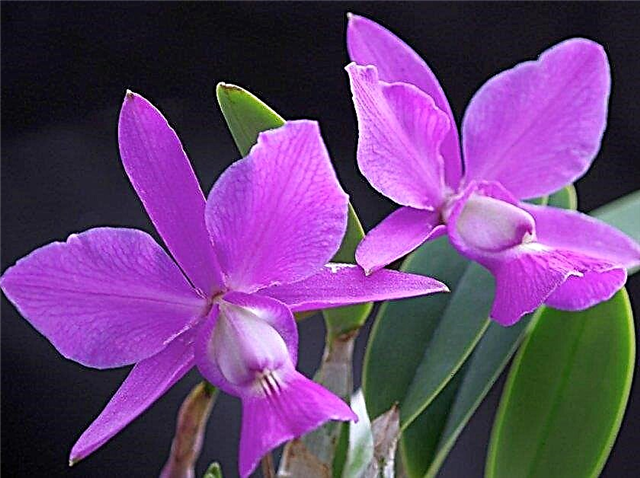

- Cumbria Gives peduncles 1-2 times per year, and flowering lasts up to 7 weeks.
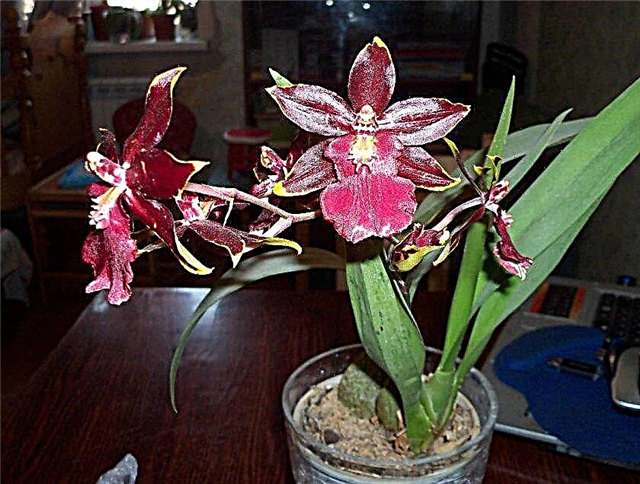

- Miltonia. Its flowering depends on the care, but is usually observed in the off-season. It lasts 3-6 weeks. Its hybrid miltassia is characterized by even longer flowering.
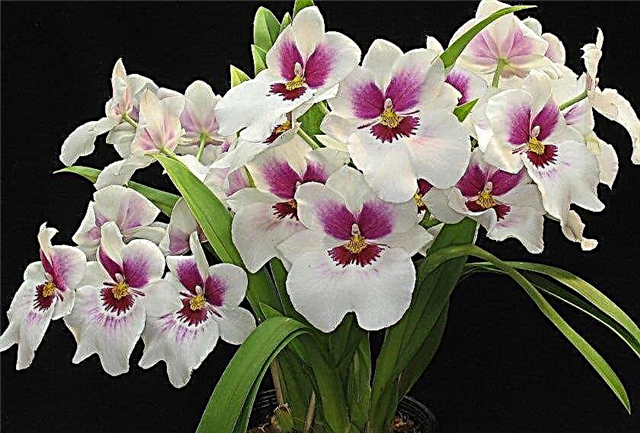

- Cymbidium. Usually blooms once a year in October and pleases with its color for up to 3 months. With good care, it can give a second color in the spring and summer.
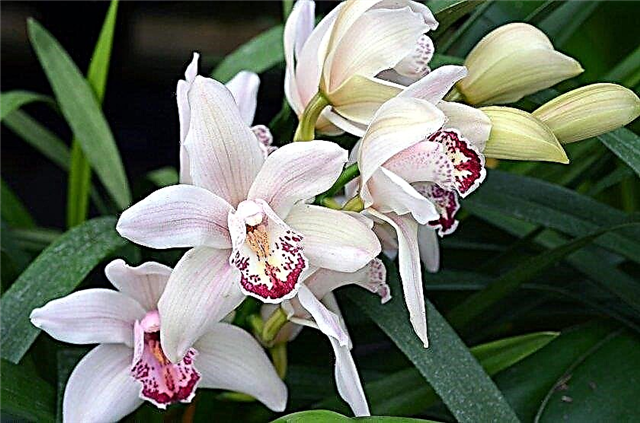

- Wanda. It blooms 1–4 times a year depending on the light regime. Each flowering lasts from 2 to 6 weeks.
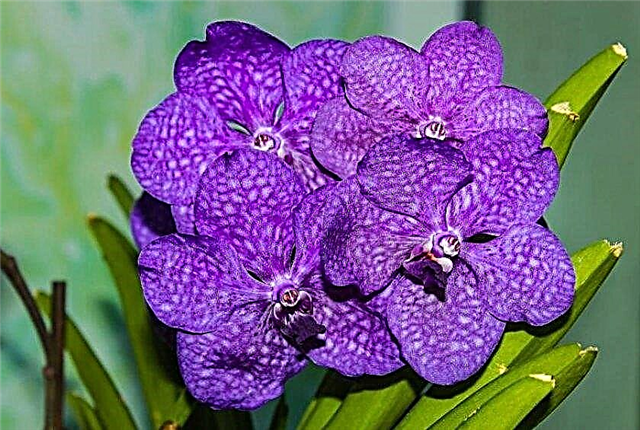

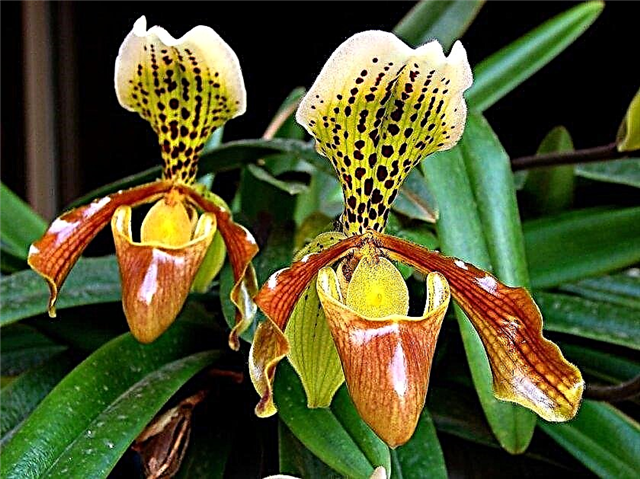
- Venus slipper. Blossoms in May-June for about 2-3 months.

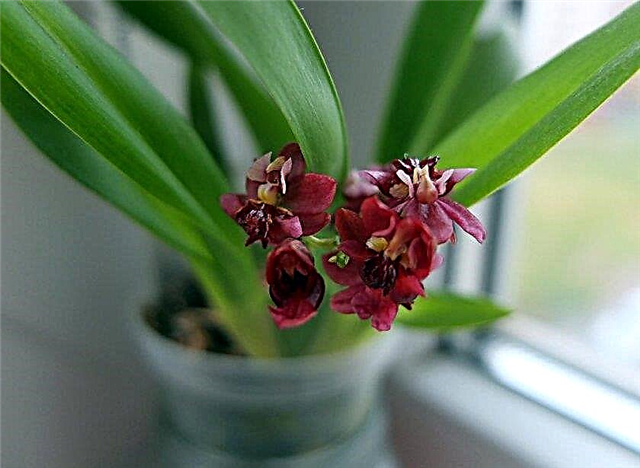
- Oncidium. It blooms once in April-July, but can bloom again in late autumn.

What to do immediately after flowering
After flowering, the arrow can be removed from sympodial (cattleya, miltonia, cymbidium, dendrobium, oncidium) orchids. In monopodial (phalaenopsis, vanda) species, faded peduncles should be left.
Trimming can be done in two ways:
- cut the plant from the base by 2.5–3 cm;
- remove the peduncle partially above the sleeping bud by 1.5–2 cm.
Did you know? Pink orchids are presented to the fairer sex for any reason. White varieties adorn celebrations, and yellow ones can be presented to colleagues at work. Colorful orchids give sweetheart.
Remove the stalk
Dry stem is usually removed. When removing the green arrow, it is worth considering that such pruning will slow the appearance and growth of new stems, since the plant's forces will focus on the development of formed buds. Usually, such pruning is done in a patient or a flower exhausted by prolonged flowering, which still let the bud go. Before carrying out the trimming process, all used tools (knife, pruning shears) should be thoroughly washed and thoroughly sanitized. It should be noted that the pruning tool should be well sharpened to accurately cut the plant and not damage it.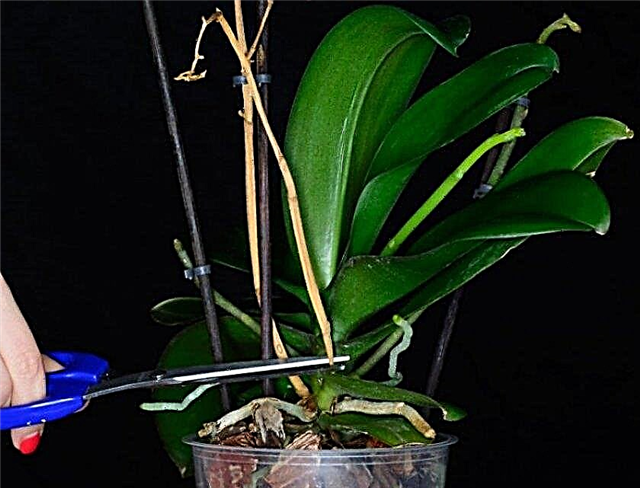 The slice should be treated with one of the following preparations - iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate, activated carbon or cinnamon powder. If the process remaining after the cut has a cavity, then it must be sealed with beeswax. This procedure will protect against ingress of water, causing the process of decay, as well as from harmful microorganisms that can damage the plant. In phalaenopsis, the green peduncle after flowering can be cut. The arrow is cut into cuttings with one kidney on each and rooted in a substrate or in water using stimulants (Epin or Zircon).
The slice should be treated with one of the following preparations - iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate, activated carbon or cinnamon powder. If the process remaining after the cut has a cavity, then it must be sealed with beeswax. This procedure will protect against ingress of water, causing the process of decay, as well as from harmful microorganisms that can damage the plant. In phalaenopsis, the green peduncle after flowering can be cut. The arrow is cut into cuttings with one kidney on each and rooted in a substrate or in water using stimulants (Epin or Zircon).
Did you know? The smallest orchid on Earth has translucent flowers with a diameter of 2.1 mm and a thickness of 1 cell. Discovered in Ecuador Cerro Candelaria Nature Reserve American botanist Lou Jost, who carried her to the genus Platystele.
Partially crop
Sometimes on the arrows after flowering, new buds begin to grow. Some species of them may develop new flowers or children (phalaenopsis, oncidiums). To stimulate repeated abundant flowering in the phalaenopsis, it is advised to cut the upper buds above the second or third bud. In this case, you should create optimal conditions for further flowering and vegetation - plenty of light, spraying, fertilizing and watering. They also keep the temperature regime for flowering with temperature differences of 5–6 ° С.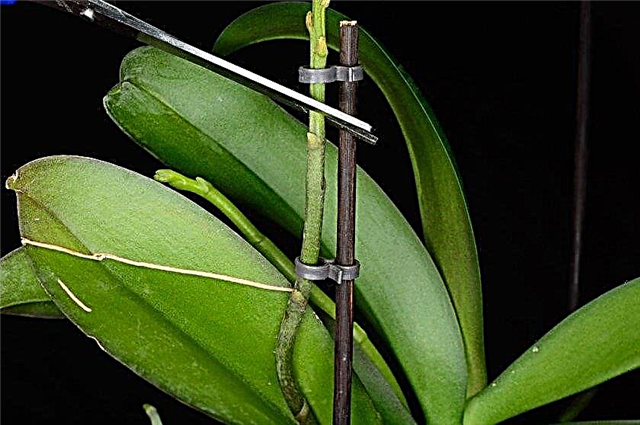
In which case can you do nothing?
In some species of orchids (phalaenopsis, vanda) flower stalks can not be pruned. They are removed only when they are completely dry, giving all their strength for further vegetation. In this case, a dormant period is created for the plant with a reduction in watering and top dressing, a slight decrease in temperature.
How to care for an orchid after flowering?
For some species that do not need a dormant period (phalaenopsis), you can do nothing but maintain optimal conditions for repeated flowering. However, some species require the mandatory organization of wintering, and the requirements for it may be different. If the plant requires replacement of the substrate, then after flowering a favorable time for its transplantation comes.
Ensuring optimal conditions
After the orchid has bloomed, it begins the period of rest, which is necessary to restore strength before the next flowering.
At this time, experts recommend adhering to the following recommendations for creating optimal conditions for a flower:
- A pot with an orchid should stand in a well-lit place, but without direct sunlight.
- Daylight hours should be around 12 hours.
- Keep the orchid away from heaters.
- Reduce watering and gradually reduce feeding.
- Humidity should be maintained, the plant should be sprayed from a spray bottle. Too dry indoor air will adversely affect the subsequent flowering of orchids. Spraying is less common at low temperatures.
- It is not recommended to transfer the orchid to another place, at least in relation to the light source.

Watering and fertilizing
Phalaenopsis can continue to be watered and fed with special fertilizers for orchids, so that the plant recovers after flowering. Cattleya and dendrobiums need to reduce irrigation and cancel or reduce feeding. Some varieties (King dendrobium) require a complete cessation of watering against a background of low temperatures.
Transfer
Often an orchid is sold in small pots, but with the presence of color, so as soon as it fades, it is necessary to transplant. For this purpose, they acquire a transparent pot 3 cm larger in diameter than the previous one. Special primers for orchids are purchased in specialized stores. If desired, you can cook it yourself: it consists of bark, moss, peat and coarse sand.
The transfer sequence is as follows:
- In order to pull the orchid out of the pot without damage, it must be well watered.
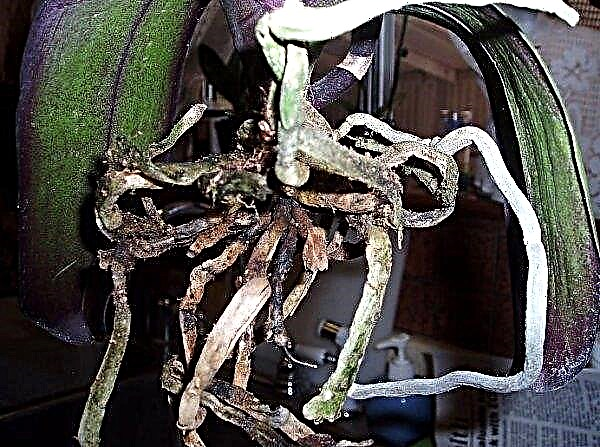
- Carefully remove the flower from the pot, rinse the roots in warm water and inspect for damage. All rotted parts of the plant should be cut and sprinkled with activated carbon powder.
- A little soil is added to the pot, then a plant is placed in it, evenly distributing the roots, and covered with prepared soil.
- The substrate should be carefully tamped.
- When planting in new land, you need to make sure that the growth point is not deepened, as this can cause the process of decay.
Video: orchid transplant
Watering begins to be carried out only after a week to give time to heal the wounds received during the transplant. After flowering of an adult plant, in which children are formed, taking root, daughter plants are separated and planted in separate small pots. Soil for planting - very small pieces of bark and a lot of moss.
Important! The transplant should be carried out in a timely manner as the orchid grows, with acidified or compacted soil, otherwise the root system will begin to rot, and the flower may die.
Features of care at rest
Most often, at such a time, flower care is carried out as usual, but the intensity of watering should be reduced and feeding should be stopped. Many types of orchids need to organize a pronounced period of rest, and for different species it is not the same. If for cattleya it is enough to reduce watering, then dendrobiums and cymbidiums also need to lower the temperature to + 10 ° C. But phalaenopsis does without wintering and if it is going to bloom again, then the temperature regime remains normal - at night no lower than + 15 ° C, during the day + 22 ... + 23 ° C. Temperature fluctuations during the rest period should usually be small - only 2-3 ° C. Then, after dormancy, more are made to stimulate flowering. In apartments, the desired temperature and its fluctuations are achieved naturally in the off-season, when the heating is not turned on. If there are temperature controllers in the heating system, then you can use them for the necessary differences. Sometimes, to achieve the desired temperatures and their fluctuations, the plant is taken out to the balcony.
Temperature fluctuations during the rest period should usually be small - only 2-3 ° C. Then, after dormancy, more are made to stimulate flowering. In apartments, the desired temperature and its fluctuations are achieved naturally in the off-season, when the heating is not turned on. If there are temperature controllers in the heating system, then you can use them for the necessary differences. Sometimes, to achieve the desired temperatures and their fluctuations, the plant is taken out to the balcony.
Did you know? According to the flower horoscope, an orchid is a flower of people born in the period from November 3 to 12. Thanks to its influence, representatives of this sign are distinguished by mystery and mystery.
Possible orchid growing problems
When growing orchids, you may encounter some problems. They are mainly caused by improper care of the plant.
Let's consider some of them:
- Fungal diseases. They are provoked by excessive watering and high humidity of the room, which is poorly ventilated, and there is no access to fresh air to the flower.
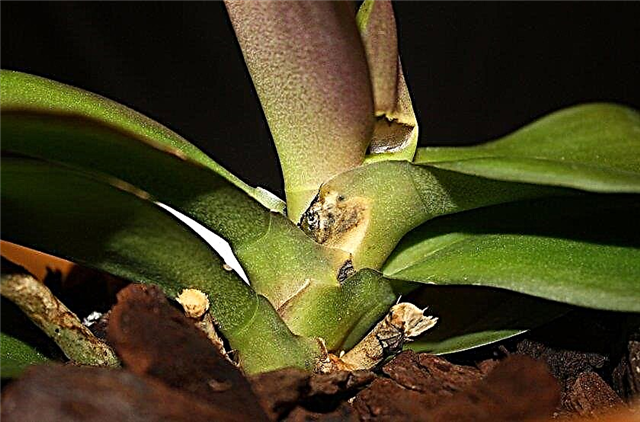

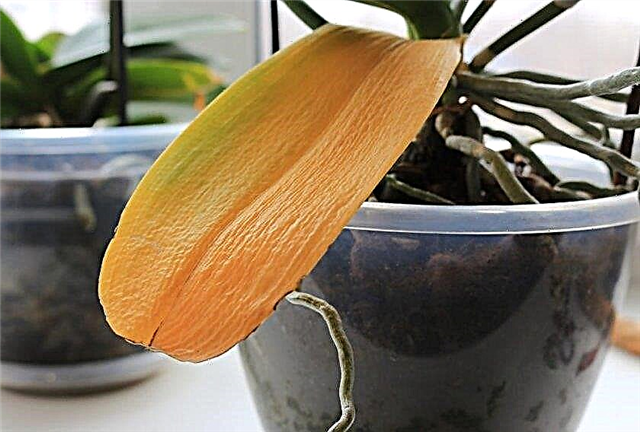
- Yellowing leaves and falling colors. This phenomenon occurs if the pot with the plant is rearranged to another place.

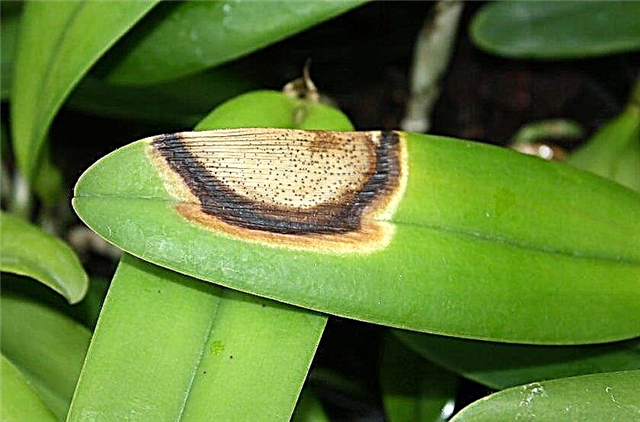
- Burns on the leaves causes direct sunlight to hit the flower.

- If the orchid looks healthy, but does not give color this indicates insufficient lighting or the absence of necessary temperature differences.
- Growth retardation as well as dry or rotten roots, lack of color, the appearance of pests - all this often signals a dry air. Of the pests, the orchid is often affected by a scab. This insect can be detected by sticky coating and the appearance of brown plaques. At the initial stage of the lesion, it is enough to gently clean the plant with a soapy solution. If this does not help, use chemical preparations (for example, Actellik).
Before taking any measures after the flowering of an orchid, you should familiarize yourself with the features of its life cycle. In some species, it is possible to achieve repeated flowering, and some need to organize a dormant period.